Protocol :
In IT industry between two computer they can communicate via network protocol.
What this network protocol : it is standard set of rules. Network Protocol
- Standard and polices made up rules
- Procedure and format defined the communication
between two device over network. In another term protocol is the digital communication between 2 devices. In practical we can consider protocol as the spoken language, if two people know their language grammar and its preposition they can communicate properly. If 2 hardware device support the same protocol even they are 2 different manufacture device(like MAC and Linux) they can communicate one another using SMTP and pop3.
Network Protocol in Detail: https://www.interserver.net/tips/kb/common-network-protocols-ports/
What are the Layers of OSI Model?
OSI Model (Open System Interconnection Model) it has 7 Layer.
- Application Layer
- Presentation Layer
- Session Layer
- Transport Layer
- Network Layer
- Data Link
- Physical
Real time world(Particle it order of layer will come in bidirectional)
Remember : AP- ST - ND - P
Application Layer
|
(http,https)- Web Surfing,(FTP) – File Transfer (SNMP,POP3,)-Email (Telnet)- Virtual Terminal
(NFS,DHCP) – Network Management Protocol.Application Layer is the topmost Layer for handling High-level protocols. Every application cannot be placed in the application layer except who communicate with other system. Ex : Text editor can't be consider into application layer.
|
Presentation Layer
|
Receive data from Application,
(Huge Audio/Video/Image/Test file convert into small file)
1)Convert the alphanumeric value into binary.
2)compression(Lossy/Lossless)
3)Also Encryption/Decrption (SSL Secure socket Layer)
Refer : https://static.javatpoint.com/tutorial/computer-network/images/osi-model3.png
|
Session Layer
|
API,NETBIOS,
(Authentication,Authorisation) – Session Authentication- This information whether
connection is Listen,Closed,Established from the netstat command
|
Transport Layer
| Control the Reliability of communication.
Data (Data Unit)
|
The data receive from Session Layer divided into small unit called segment
|
Segmentation
|
Contain 1)source port 2)Destination Port 3)Sequence number
- port number used to coordinate with correct application
- sequence number is used to resemble the data to deliver message at the receiver side.
|
Flow Control
|
Amount of data to transfer, between max speed.(Best possibility device supported speed at
the bidirectional)
|
Error Control
|
Checksum + added to the Data(To find whether is it corrupted or not).
|
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vv4y_uOneC0&t=487s
Transport Layer has 2 protocol
|
TCP
|
UDP
|
Connection(Establishes a connection
between the computer before transmit the data)
-Header 20 Bytes(heavy Weight)
|
Connection-less (UDP directly send to the destination
computer without checking the system is ready to
receive or not)-it is 8 Bytes(Less weight)
|
SLOW– ACK/retranmit the data if lost
FTP
|
FAST -NO ACK/re-transmit the lost data.
Email
|
TCP is reliable as it guarantees delivery of data
|
Delivery of the data to the destination cannot be guaranteed
|
TCP is comparatively slower
|
UDP is faster,Simpler and more efficient than TCP.
|
Does not provide broadcasting(Stream based)
|
UDP support Broadcasting
|
SSH,http,https(www),FTP,Telnet,
SSH,IMAP,SMTP can use it either UDP/TCP.
|
DNS,DHCP,TFTP,VOIP,BOOTPBootstrap Protocol)
|
Applicable: Reliable
|
Fast
|

Picture
https://techdifferences.com/
wp-content/uploads/2016/04/TCP.jpg
|

https://techdifferences.com/
wp-content/uploads/2016/04/UDP.jpg
|
|
Network Layer
|
1)Logical Addressing(IPV4/IPV6) 2)Routing 3)Path Determination (Data Packet)
|
Data Link
|
Logical IP address map into Physical Layer. [ Data Packet + MAC Address -> Data Frame ]
Tail + header add header
|
Physical
|
Convert bit into signal.(depends on the media, Ethernet, Air)
|
Source : http://teachweb.milin.cc/images/datacommunicatie/introduction_to_networks/6.1.1.1_the_network_layer_small.gif
Characteristics Behaviour of OSI 7 Layer
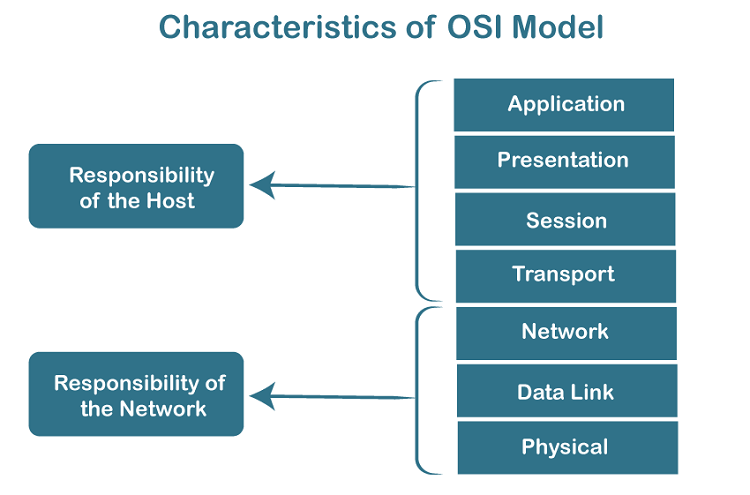 |
Source https://static.javatpoint.com/tutorial/computer-network/images/osi-model.png |
Refer:
https://www.javatpoint.com/computer-network-tutorial
Data Packets -> contain Segment , IP
What is Packet: (Packet will go through layer 3 – Network Layer)
- Source IP Address
- Destination IP Address
- Data
- CRC
- Type
What is Data Frame: (Network Layer Packet + MAC Address)
- Source IP + MAC Address
- Destination IP + MAC Address
- Data
- CRC
- TYPE
- This adding MAC Address consider as the Header(H1) + Tail(T1) to the packet and become Frame.
- Depends on the medium these Header/Tail will be added and alter the frame later also, Because when it is Moving from wireless to the satellite New satellite header(H2)/tail(T2) will be added.
- Refer : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vv4y_uOneC0 (13:00 - Get clear details)
Transport Layer | Network Layer | Data Link Layer | Physical Layer

Layer
|
Protocol
|
Device
|
7. Application
|
(http,https)- Web Surfing,(FTP) – File Tran-fer (SNMP,POP3,)-
Email (Telnet)- Virtual Terminal (NFS,DHCP) –
Network Management Protocol.
|
|
6. Presenatation
|
Compression,Decryption
|
|
5.Session
|
Log on / Log off
|
|
4.Transport
|
TCP,UDP – Prepare Packet
|
|
3.Network
|
IP + Packet
|
Routers
|
2.Data Link
|
802.3,802.5 – IP + Packet + Mac
|
NIC,Switches,Bridges,WAPS
|
1.Physical
|
100BASE-T,1000BASE-X
|
Hubs,patch panels,RJ-45 jack
|
Gateway become router. But router doesn’t become gateway.
- Gateway act as “gate” between two network.
- Act as router,firewall(block/allow)
- Enable traffic to flow in and out of the network.
- Proxy server is another type of gateway.
- Inside the gateway Hardware,it contains the software.But, Router providing function of routing IP packets between networks.
Gateway and router both are not same.
Router and Gateway is intelligent than switch, Because it send the packet exactly to the destination rather than multicast.
|
|
Above Image Referecehttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZvWn5xBflUs
Router Vs Switch
|
Reference URL :https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1z0ULvg_pW8

|
|
|
 |
|
|

|
Further Studies Focus on :
How This TCP/IP fundamental apply in the real time world.
1)Create the firewall 2)Setup the network/net mask
Study ;
Whether TCP header/tail is included (I hope it is in Data link then why physical layer).









0 Comments